MCP server(s) for agentic AI with IBM i
Overview
The IBM i MCP Server enables AI agents to interact with IBM i systems through the Model Context Protocol (MCP). It provides secure, SQL-based access to Db2 for i databases, allowing AI applications like Claude, VSCode Copilot, Bob, and custom agents to query system information, monitor performance, and execute database operations.
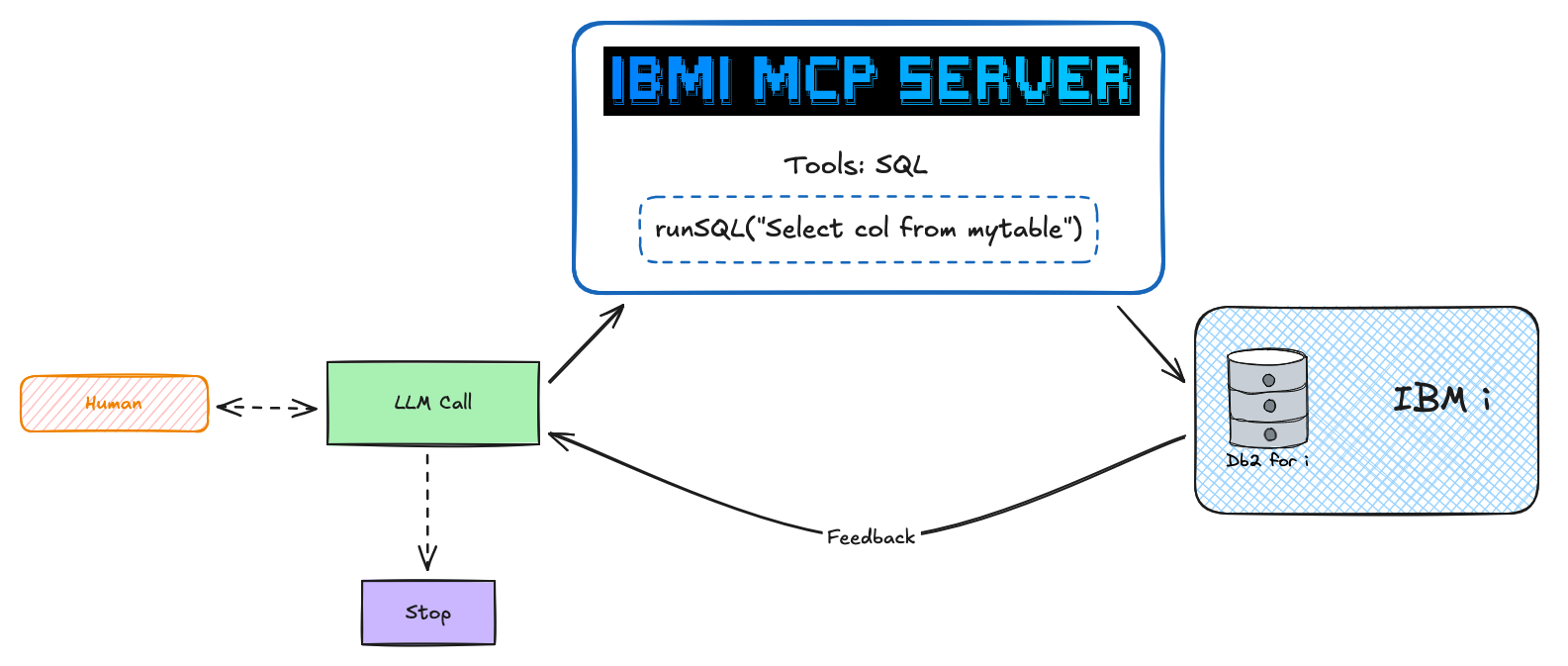
How it works: AI clients connect via MCP → Server executes YAML-defined SQL tools → Results stream back to the AI agent through Mapepire.
📁 Repository Structure
| Directory | Purpose | Documentation |
|-----------|---------|---------------|
| server/ | MCP server implementation (TypeScript) | Server README |
| tools/ | YAML-based SQL tool configurations | Tools Guide |
| agents/ | AI agent examples and integrations | Agents Guide |
| client/ | Python client examples for testing | Client README |
| deployment/ | Docker, Podman, OpenShift configs | Deployment Guide |
📖 Quick Navigation
- 🚀 MCP Server - Get started with the server
- 🧩 SQL Tools - Create custom SQL tools
- 🤖 AI Agents - Use agent frameworks
- 🐍 Python Clients - Test with Python clients
- 📦 Deployment - Deploy to production
- 📡 Setup Mapepire - Install prerequisite
🚀 MCP Server
The MCP Server enables AI agents to execute SQL queries on IBM i systems through YAML-defined SQL tools.
Quick Start
Prerequisites:
- Mapepire installed on IBM i
- Node.js 18+ installed
Steps:
-
Create configuration file:
cat > .env << 'EOF' DB2i_HOST=your-ibmi-host.com DB2i_USER=your-username DB2i_PASS=your-password DB2i_PORT=8076 DB2i_IGNORE_UNAUTHORIZED=true EOF -
Run the server:
export MCP_SERVER_CONFIG=.env npx -y @ibm/ibmi-mcp-server@latest --transport http --tools ./tools -
Verify it's running:
curl http://localhost:3010/healthz
What You Can Do
- Connect AI Clients: Claude Desktop, VSCode Copilot, Cursor, Windsurf, and more
- Execute SQL Tools: Run pre-configured or custom SQL queries via MCP (
--tools) - Monitor IBM i Systems: Performance, jobs, security, storage, and more
- Build Custom Tools: Create YAML-based SQL tools for your specific needs
[!NOTE] 📖 Full Documentation: Server README →
Quick Links:
🧩 SQL Tools
YAML-based SQL tool configurations that define what queries AI agents can execute on your IBM i system.
Quick Start
Create a custom tool file tools/my-tools.yaml:
sources:
my-system:
host: ${DB2i_HOST}
user: ${DB2i_USER}
password: ${DB2i_PASS}
port: 8076
ignore-unauthorized: true
tools:
system_status:
source: ibmi-system
description: "Overall system performance statistics with CPU, memory, and I/O metrics"
parameters: []
statement: |
SELECT * FROM TABLE(QSYS2.SYSTEM_STATUS(RESET_STATISTICS=>'YES',DETAILED_INFO=>'ALL')) X
toolsets:
performance:
tools:
- system_status
Run the server with your tools:
npx -y @ibm/ibmi-mcp-server@latest --tools ./tools/my-tools.yaml --transport http
Available Tool Collections
The tools/ directory includes ready-to-use configurations:
- Performance Monitoring - System status, active jobs, CPU/memory metrics
- Security & Audit - User profiles, authorities, security events
- Job Management - Active jobs, job queues, subsystems
- Storage & IFS - Disk usage, IFS objects, save files
- Database - Tables, indexes, constraints, statistics
🤖 AI Agents
Pre-built AI agent examples using popular frameworks to interact with IBM i systems through the MCP Server.
Available Agent Frameworks
| Framework | Language | Use Case | Documentation | |-----------|----------|----------|---------------| | Agno | Python | Production-ready agents with built-in observability | Agno README | | LangChain | Python | Complex workflows and tool chaining | LangChain README | | Google ADK | Python | Google AI ecosystem integration | Google ADK README |
What Agents Can Do
- System Monitoring: Real-time performance analysis and health checks
- Troubleshooting: Diagnose issues using natural language queries
- Reporting: Generate system reports and insights
- Automation: Execute administrative tasks through conversation
🐍 Python Clients
Simple Python client examples for testing and interacting with the MCP Server.
import asyncio
from mcp import ClientSession
from mcp.client.streamable_http import streamablehttp_client
async def main():
# Connect to the IBM i MCP server with authentication
async with streamablehttp_client("http://localhost:3010/mcp") as (
read_stream,
write_stream,
_,
):
# Create a session using the authenticated streams
async with ClientSession(read_stream, write_stream) as session:
# Initialize the connection
await session.initialize()
# List available tools (now authenticated with your IBM i credentials)
tools = await session.list_tools()
for i, tool in enumerate(tools.tools, 1):
print(f"{i:2d}. {tool.name}")
print(f" └─ {tool.description}")
# Execute a tool with authenticated IBM i access
print("\n" + "=" * 80)
print("SYSTEM ACTIVITY RESULT")
print("=" * 80)
result = await session.call_tool("system_activity", {})
print(result)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
📦 Deployment
Production-ready deployment configurations for containerized environments.
Deployment Options
- Docker & Podman - Complete stack with MCP Context Forge Gateway
- OpenShift - Kubernetes deployment with S2I builds
- Production Features - HTTPS, authentication, monitoring, caching
📡 Setup Mapepire
Before you can use the ibmi-mcp-server, you must install and configure Mapepire on your IBM i system.
What is Mapepire?
Mapepire is a modern, high-performance database server for IBM i that provides SQL query execution capabilities over WebSocket connections. It acts as a gateway between modern application architectures (like MCP servers, AI agents, and REST APIs) and IBM i's Db2 for i database.
Why Mapepire Enables AI and MCP Workloads
Traditional IBM i database access methods (ODBC, JDBC) don't align well with modern AI and MCP architectures that require:
- Fast, lightweight connections: AI agents make frequent, short-lived database queries
- WebSocket support: Enables real-time, bidirectional communication for streaming results
- Modern JSON-based protocols: Simplifies integration with TypeScript/JavaScript ecosystems
- Low-latency responses: Essential for interactive AI conversations and tool executions
Mapepire bridges this gap by providing a modern, WebSocket-based SQL query interface that's optimized for the request/response patterns of AI agents and MCP tools.
Installation
Quick Install (IBM i SSH Session):
# 1. Install Mapepire using yum
yum install mapepire-server
# 2. Install Service Commander (if not already installed)
yum install service-commander
# 3. Start Mapepire service
sc start mapepire
[!NOTE] 📚 Full Documentation: Mapepire System Administrator Guide →
[!IMPORTANT] Important Notes:
- By default, Mapepire runs on port
8076. You'll need this port number when configuring theDB2i_PORTvariable in your.envfile.- Ensure your IBM i firewall allows inbound connections on port 8076
- For production deployments, configure SSL/TLS certificates (see official guide)
📜 License
This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0. See the LICENSE file for details.






