Automate Blender 3D modeling from n8n using MCP. 45+ tools for modeling, materials, lighting, rendering, and animation.
Blender MCP Server for n8n
A Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that exposes Blender's 3D modeling capabilities to n8n workflows via HTTP SSE transport.
Quick Start
1. Install Dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txt
Installation
Method 1: Zip & Install (Recommended)
- Zip the
blender_mcp_addonfolder (intoblender_mcp_addon.zip). - Open Blender.
- Go to Edit > Preferences > Add-ons.
- Click Install... and select the
.zipfile. - Search for "Blender MCP" and enable the checkbox.
Method 2: Manual Copy (Developer)
- Copy the
blender_mcp_addonfolder to your Blender addons directory:- Windows:
%USERPROFILE%\AppData\Roaming\Blender Foundation\Blender\4.x\scripts\addons - macOS:
~/Library/Application Support/Blender/4.x/scripts/addons
- Windows:
- Restart Blender.
- Enable "Blender MCP" in Preferences.
Why a folder instead of a single file?
As the addon grows, a single 1800+ line file becomes unmaintainable. We've split the logic into functional modules (modeling, materials, anim, etc.) to make it professional, readable, and easier to extend.
Usage
1. Configure n8n Workflow
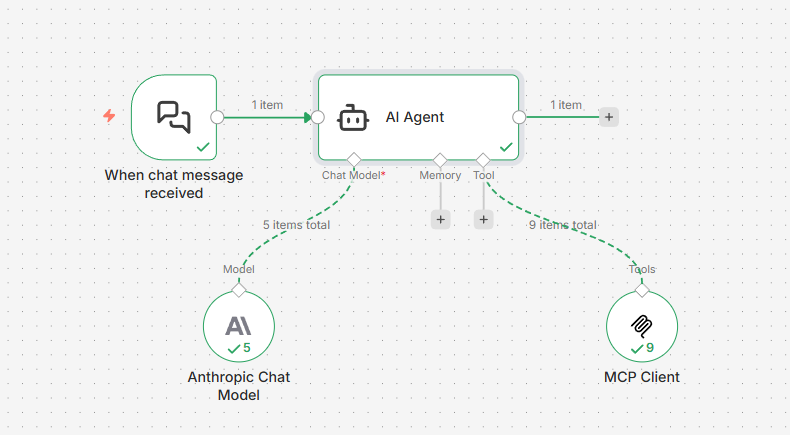
- Open the N Panel (press
Nin the 3D Viewport). - Look for the Blender MCP tab.
- Click Start MCP Server.
2. Updating & Applying Changes
If you modify the addon code or the MCP server logic, follow these steps to ensure changes are applied:
- Reload Scripts: In Blender, press
F3and type "Reload Scripts" (or use the shortcutAlt + Rif configured). - Restart Blender Server: In the N-Panel, click Stop MCP Server and then Start MCP Server again.
- Restart Python Server: Stop and restart the server with
python -m src.main.
[!IMPORTANT] All Blender operations now run on the main thread via a command queue, ensuring stability and preventing dependency graph errors.
3. Start the MCP Server
python -m src.main
The server will start on http://localhost:8000 with SSE endpoint at /sse. It uses detailed logging to show exactly which tools are being called and their results.
4. Configure n8n
In your n8n workflow:
-
Add MCP Client Tool node
-
Configure:
- SSE Endpoint:
http://localhost:8000/sse - Authentication: None
- Tools to Include: All
- SSE Endpoint:
-
Connect to an AI Agent node
Available Tools
The server exposes 45+ Blender tools across several categories:
Scene & Inspection
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| get_scene_info | Get information about the current Blender scene (objects, collections, etc.). |
| get_object_info | Get detailed information about a specific object. |
| get_viewport_screenshot | Capture a screenshot of the 3D viewport. |
| get_distance | Measure the distance between two objects. |
| get_debug_info | Get diagnostic information about the MCP server. |
Collections
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| create_collection | Create a new collection in the scene. |
| set_active_collection | Set the active collection for new objects. |
| move_to_collection | Move objects to a specific collection. |
| get_collections | Get the hierarchy of all collections in the scene. |
Modeling
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| create_cube | Create/update a cube mesh. |
| create_cylinder | Create/update a cylinder mesh. |
| create_sphere | Create/update a UV sphere mesh. |
| create_icosphere | Create/update an Ico sphere mesh. |
| create_torus | Create/update a torus mesh. |
| create_plane | Create/update a plane mesh. |
| duplicate_object | Duplicate an object with optional transformations. |
| create_and_array | Create a primitive and apply a linear array modifier in one step. |
| batch_transform | Transform multiple existing objects at once. |
| apply_modifier | Add and configure a modifier (ARRAY, SOLIDIFY, BEVEL, etc.). |
| copy_modifier | Copy a modifier from a source object to targets. |
| remove_modifier | Remove a modifier from an object. |
| boolean_operation | Perform INTERSECT, UNION, or DIFFERENCE between objects. |
| transform_object | Transform an existing object (location, rotation, scale). |
| circular_array | Create objects arranged in a circular/radial pattern. |
| select_objects | Select multiple objects by name. |
| select_by_pattern | Select objects matching a glob pattern (e.g., 'Facade_Fin*'). |
| set_object_dimensions | Set exact dimensions for an object in meters. |
| join_objects | Join multiple objects into a single mesh. |
| random_distribute | Randomly distribute copies of an object with constraints. |
Materials
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| create_material | Create a material with PBR presets and assign it to objects. |
| assign_material | Assign an existing material to objects or patterns. |
| set_material_properties | Modify properties of an existing material. |
| add_shader_node | Add a shader node to a material's node tree. |
| connect_shader_nodes | Connect two shader nodes in a material. |
| assign_builtin_texture | Apply a procedural texture to a material. |
Animation
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| set_keyframe | Set a keyframe for an object property at a specific frame. |
| get_keyframes | Get all keyframes for an object. |
| set_timeline_range | Set the start, end, and current playback frames. |
| play_animation | Start or stop animation playback. |
Rendering
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| configure_render_settings | Set render engine, samples, and resolution. |
| render_frame | Render the current frame to a file. |
| render_animation | Render an animation sequence to a directory. |
Camera
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| create_camera | Create a new camera in the scene. |
| set_active_camera | Set the active camera for the viewport and rendering. |
| camera_look_at | Point a camera at a target location. |
Lighting
| Tool | Explanation |
|---|---|
| create_light | Create POINT, SUN, SPOT, or AREA lights. |
| configure_light | Update light properties like energy, color, and size. |
Example Usage in n8n
Use natural language with the AI Agent:
- "Create a red metallic sphere at position [0, 0, 2]"
- "Duplicate 'Base_Slab', move it to Z=80, and remove its Array modifier"
- "Select both the glass and railing, then copy the Array modifier from the glass to the railing"
- "Add a torus with minor_radius 0.1 and major_radius 25"
Examples
Check out our step-by-step examples to see the server in action:
- Condominium Tower: A complete guide to creating a procedural 20-story building with glass facade and balconies.
Configuration
Set environment variables in .env:
BLENDER_MCP_HOST=127.0.0.1
BLENDER_MCP_PORT=9877
BLENDER_ASSETS_DIR=C:/path/to/your/assets
Architecture & Technical Design
This project uses a modular src/ structure to ensure maintainability:
graph TD
A[main.py] --> B[server.py]
B --> C[tools/ package]
C --> D[modeling.py]
C --> E[scene.py]
C --> F[materials.py]
B --> G[connection.py]
G --> H[Blender]
Transport Model
Although the MCP specification supports persistent SSE sessions, many clients (including n8n) currently operate in a stateless execution model, performing:
Initialize → Discover Tools → Call Tool → Close
for each interaction.
The server therefore supports:
- SSE session mode: For fully stateful MCP clients.
- Stateless JSON-RPC fallback: For per-call execution clients like n8n.
The Stateless Fallback Mechanism
To ensure reliability across clients, the server implements a robust fallback strategy:
- Protocol Resilience: If no active SSE session exists, the server transparently handles standard JSON-RPC requests over HTTP.
- Execution Isolation: Each tool call is processed independently, preventing session corruption or deadlocks.
- Visual Success Indicators: Tool responses are prefixed with
✓when successful. This helps the AI Agent’s conversational memory confirm task completion and avoid unintended re-execution loops. - Clear State Boundaries: Persistent state is intentionally separated:
- 🧠 Conversation memory → AI Agent (n8n Simple Memory)
- 🧩 Scene state → Blender runtime
- 🚀 MCP server → Stateless execution bridge
Architecture Diagram
n8n AI Agent
↓
MCP Client (Stateless JSON-RPC)
↓
MCP Server (ASGI)
↓
TCP Socket Bridge
↓
Blender Addon (Main Thread Queue)
↓
Blender Scene (Persistent State)
Troubleshooting
Server won't start: Install dependencies with pip install -r requirements.txt
Connection failed: Ensure Blender MCP addon is running on port 9877.
Dependency Graph Error: If you see this, ensure you have the latest blender_mcp_addon package which implements the main-thread command queue.
Tools not appearing in n8n: Check the SSE endpoint URL is correct (http://localhost:8000/sse)
Acknowledgments
This project was inspired by blender-mcp by [ahujasid], which demonstrated the potential of MCP servers for Blender automation.
License
MIT License - See LICENSE file for details